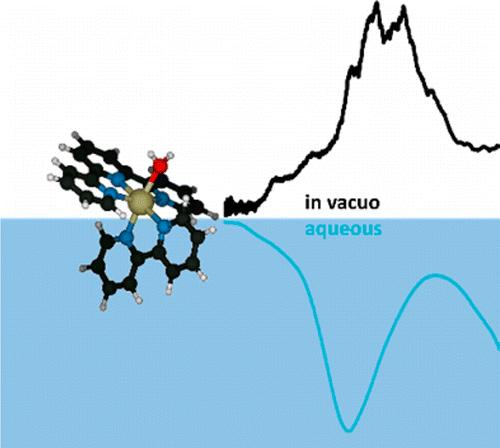
Ruthenium(II) complexes are of great interest as homogeneous catalysts and as photosensitizers; however, their absorption spectra are typically very broad and offer only little insight into their electronic structure. We present the electronic spectrum of the aquo complex [(trpy)(bipy)RuII–OH2]2+ measured by photodissociation spectroscopy of mass-selected ions in vacuo (bipy = 2,2′-bipyridine and trpy = 2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine). In the visible and near-UV, [(trpy)(bipy)RuII–OH2]2+ has several electronic bands that are not resolved in absorption spectra of this complex in solution but are partially resolved in vacuo. The experimental results are compared with results from time-dependent density functional theory calculations.
Shuang Xu†‡ and J. Mathias Weber*†§
† JILA, University of Colorado, 440 UCB, Boulder, Colorado 80309, United States
‡ Department of Physics, University of Colorado, Boulder, Colorado 80309, United States
§ Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of Colorado, Boulder, Colorado 80309, United States